What is Post-Secondary Education?

quick answer
Canada has three post-secondary school categories: college, university, and institute. A post-secondary education can earn you a Degree, Diploma, Certificate, or other credentials. Only certified Canadian post-secondary schools can grant these qualifications.
In This Article
Post-secondary enrollment in Canada has grown substantially over the years with nearly 2.5 million students enrolled in 2019 alone. But what is post-secondary education in Canada?
Post-secondary education, or tertiary education, is the highest form of educational standing. In Canada, this includes colleges, universities, and institutes. Available qualifications include Degrees, Diplomas, Certificates, and other post-secondary credentials.
While it’s most common to secure your High School Diploma before beginning, there are many ways to receive a post-secondary education without following the traditional path. Requirements vary depending on your province and institution, but a few options include:
Here, we’ll explain everything you need to know about post-secondary education, from associated costs to consider and certification types to the biggest differences between provinces. This will give you an idea of how to pursue a meaningful career with a Canadian post-secondary education.
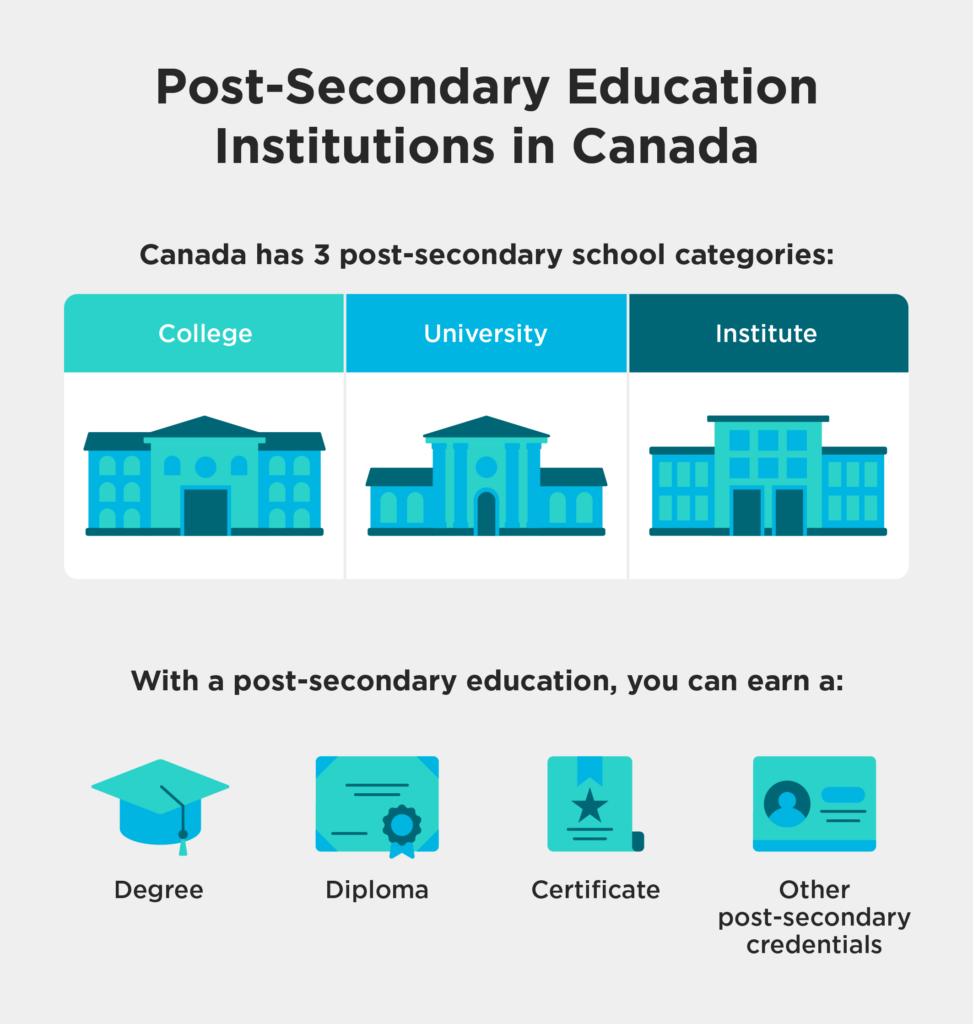
You can guess most post-secondary schools’ type by their name. It will usually include “college, university, or institute” in their name. But this can be confusing when people use terms like college and institute to describe the same thing. On top of this, most post-secondary schools now offer a wide range of certifications like Project Management, or Web Development.
We’ve outlined the main differences between colleges and universities and institutes. Let’s find out what each type of school can offer in terms of certifications, programs, and more.
In Canada, colleges are considered different from universities because they do not offer Degrees. This includes “college,” “community college,” or a “College of Applied Arts or Applied Technology.”
Colleges offer programs that develop practical skills for a job or industry. These programs are for students who want to find work in industries like Business, Trades, Health Care, Community Services, and more.
Colleges can offer the following certifications:
Certificate programs can be as short as five months or as long as one year, whereas Diploma programs usually range from one to three years. Every college and institute is different, but Diploma programs typically take longer to complete than Certificate programs.
In some college semesters, you could be taking upwards of eight courses per term. Colleges will typically create a schedule based on the core courses of your program. This schedule will also include your choice of electives, which are unrequired courses. Colleges have a lot of classroom-centered activities, such as power tool safety workshops or cosmetology skills labs. Hands-on learning environments come with less flexible schedules in this regard.
Most universities are easy to spot as they will have the word “university” in the school’s name. There are exceptions to this rule, such as NSCAD (Nova Scotia College of Art and Design University) and OCAD (Ontario College of Art & Design University). These institutions chose to keep their recognizable college names when they received a university status.
Universities offer a broad range of subjects for students to choose from. University programs can help develop practical skills, but they also offer more complex and theoretical programs. Many students choose university so they can dive deep into research that may or may not have practical applications.
Universities can grant Certificates, Diplomas, Degrees, and other certifications. But the ability to grant Degrees is one of the biggest differences between college and university. The three types of university Degrees available include:
If you attend university, you’re in charge of creating your own schedule and registering for courses. Students can receive guidance and advice from academic services, but what you choose to study it’s largely up to you. You get to decide how many courses you want to take per semester, and attendance requirements may be flexible depending on the program.
Full-time students take 60% or more of a full course load for their program. Part-time students take less than 60%. Between class and studying, a full-time student might spend between 30–50 hours on course work each week.
There is no official Canadian definition for “institute” in comparison to colleges and universities. Since institutions don’t usually offer Degrees, people will often use the term interchangeably with college. Privately owned colleges, “career colleges”, “Institutes of Technology or Science”, and polytechnic programs will often use the term Institution.
Privately owned institutes are reviewed and recognized by a provincial or territorial government, just like all post-secondary institutions in Canada.
Institutes offer the following certifications:
You are considered a full-time student at an institute when you take 60% or more of a full course load for your program. For example, 20+ hours of instruction per week at a private career college would make you a full-time student.
Benefits of Post-Secondary Education
Post-secondary education is important in the job market where expectations can be high for job seekers. But there are more benefits than just higher paying jobs and preparation for your career.
Your time in school can be just as valuable as the Diploma or Certificate you receive. You can meet lots of people and gain access to resources that will benefit your career in the long term. The top benefits of completing your post-secondary education include:
The cost of post-secondary education depends on the type of school you attend and the program you choose. Tuition can also be much more expensive for international students. Altogether, students need to consider the cost of:
According to Statistics Canada, the average yearly tuition fees for full-time Canadian students in 2022–2023 are as follows:
Looking into Canadian post-secondary education statistics can provide useful insights that help guide your decision making process. It’s like going for a hike in the woods — you should get a map of the educational landscape before choosing a path.
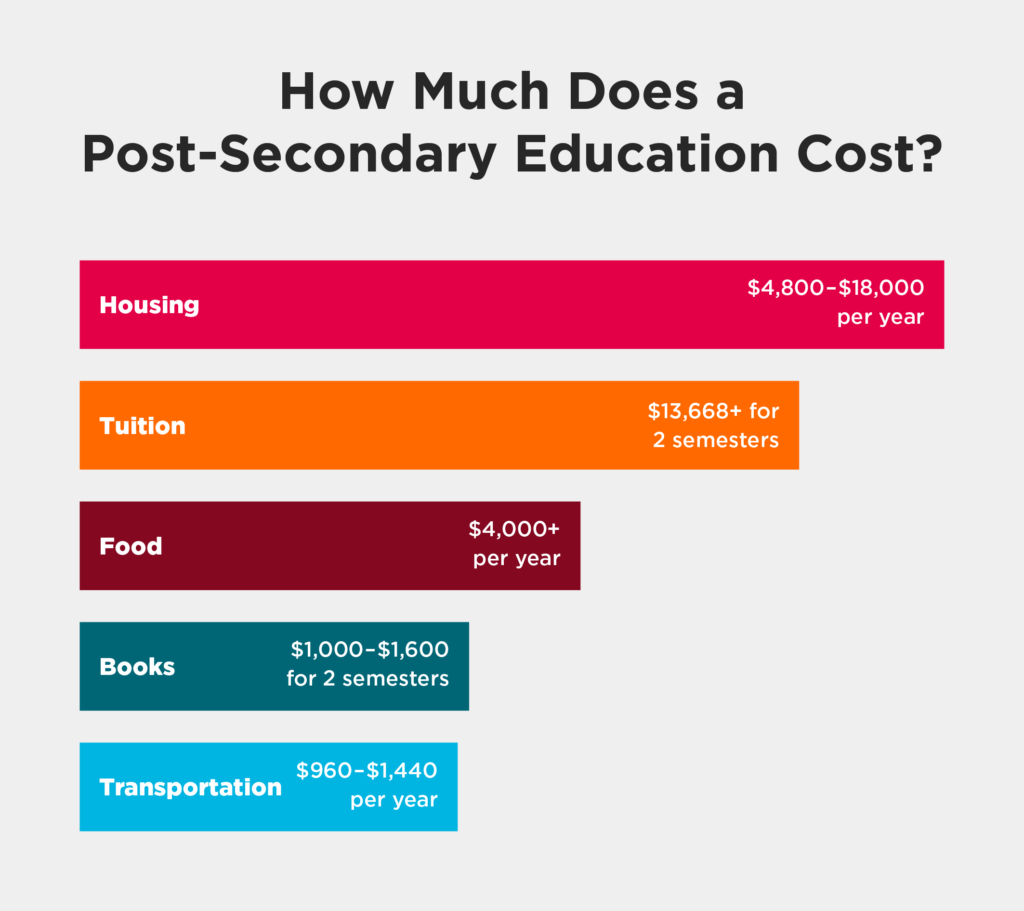
The average cost of post-secondary tuition in Canada is $6,834 per semester for Undergraduate programs, and $7,437 per semester for Graduate programs. Your chosen field of study greatly affects your tuition fees. For example, the average Undergraduate tuition fee for Dentistry is around $23,963. Associated costs for textbooks can range from $500–$1,000, depending on the requirements of your program.
International students pay much more than Canadian students. As with Canadian students, this varies greatly depending on the chosen field of study. International students may need to apply for a study permit. Study permits cost $150 per person initially, and $350 for renewals.
The province where you study will also determine the cost of tuition. Some of the highest tuition fees are in British Columbia, Nova Scotia, and Ontario. According to Statistics Canada, Graduate students in Nova Scotia pay 42.4% more than other Canadian students on average.
Other costs for education include housing, transportation, and food. The province where you study will impact how much you spend.
Dormitory housing allows students to reside close to campus, which can minimize transportation and utility costs. Apartment rentals provide more options for student housing. The cost of utilities and transportation depends on the location of your apartment. Homestay programs are available for international students who want to live in a Canadian household during their schooling. This is a great opportunity to improve English skills, learn about Canadian culture, and meet new people. Speak to your school, or use a homestay network website, for more information.
Transportation costs depend on your province and local area. Living in a dorm or taking online courses can reduce the cost of transportation. On average, transportation costs $80-$120 per month. There are student discounts available for public transportation in Canada. Your tuition may include a discounted pass, or you can purchase a discounted pass on your own with an official student ID card.
Food costs should be top of mind for students on a budget. A woman aged 19–30 years in Canada will spend $300 a month on groceries, according to Canada’s Food Price Report 2023. Some provinces have more expensive groceries food costs than others, and this is generally due to transportation requirements.
While the cost of a post-secondary education can be intimidating, there are many ways to manage and even lower your costs. For example, students can write off expenses related to their education when filing their taxes, so be sure to document your spending and keep all of your receipts.
Student loans are available to help cover the cost of tuition and associated expenses for student living. You can apply for a student loan through your provincial student loan program, and they will also contact the federal student loan program. Next, they assess your application and decide how much money you should receive. What’s great to know is that as of April 1, 2023, Canada Student Loans will no longer accumulate any interest.
You may also be eligible for grants, bursaries, scholarships, and awards. Unlike loans, there is no expectation for you to pay these back. Depending on what you receive, there may be performance requirements to continue receiving the scholarship. This is entirely dependent on the scholarship you receive. You can find more information on available scholarships and more through your provincial student loan website. Here is a list of the official provincial student loan program websites:
Universities are considered a post-secondary school in Canada. But the term “post-secondary” refers to more than just universities. The other two types of post-secondary schools are colleges and institutes.
When a job requires you to have post-secondary education, they are referring to any qualifications granted by a university, college, or institution.
No, grade 12 is not the same as a post-secondary education. A successful completion of grade 12 will earn you a High School Diploma, which is considered secondary education.
Quebec is a unique exception because their secondary education ends with grade 11. Grade 12 is an optional year where students can achieve an Ontario Secondary School Diploma (OSSD). The OSSD Diploma is not technically a post-secondary education, but students can apply the credits in a post-secondary school.
Canada has no governing body for post-secondary education at the federal level. Instead, Canadian provinces and territories are responsible for education at all levels. Each province and territory can have multiple ministries or departments for education. Here is a list of the education ministries and departments for each province and territory:
The best post-secondary education is one that matches your strengths and your goals. A Degree takes about four years to achieve and it’s a great way for people to build subject knowledge through research. Students can earn a Diploma or Certificate within a year, which is perfect for career-minded people who want to start work as soon as possible.
Apply to Robertson College today and let us help you find meaningful work with a post-secondary education based on your interests.
In This Article
Once you take the first step, one of our Student Admissions Advisors will get in touch to better understand your goals for the future.
Apply Now